A special issue curated by Kati Curts and Alex Kaloyanides
Volume 6: Issue 3 Characterizing Material Economies of Religion in the Americas
A special issue curated by Kati Curts and Alex Kaloyanides
 Characterizing Material Economies of Religion in the Americas: An Introduction
Characterizing Material Economies of Religion in the Americas: An Introduction
Kati Curts and Alex Kaloyanides introduce this special issue of MAVCOR Journal devoted to examining four key categories: “Material,” “Economies,” “Religion,” and “America(s).” The ambition of this issue is that the collective inquiries of its authors, which span various interpretive histories and genealogical fragments, can offer ways to better understand their assorted conveyances, as well as the powerful grip of their critical conjunction.
 Medals, Memory, and Findspots
Medals, Memory, and Findspots
For many Indigenous people of Turtle Island, also known as North America, treaty medals are material reminders of sacred promises made between their nations and the British Crown or the U.S. Government. Settlers and colonial officials, by contrast, have often treated these medals as mere trinkets.
 Julia Greeley, Denver’s Angel of Charity
Julia Greeley, Denver’s Angel of Charity
More than a portrait of a holy person, an icon structures a present encounter with a saint and the community that the saint represents. What kind of encounter does Greeley’s icon conjure with race and Catholicism in the Old West?
 Hilma af Klint's Temple for the Paintings
Hilma af Klint's Temple for the Paintings
Through Af Klint’s journal entries and sketches, we can shift analyses of sacred space from the guise of transcendent force that simply “appears,” in the phenomenological nomenclature, and instead approach it as technique.
 Tree Rings and Blood Lines
Tree Rings and Blood Lines
These redwood rings are both family trees and family circles, literally naturalizing a canonical “American” familial heritage insistently recited and instantiated in many media and locations: artistic and built environments, judicial practice, legislation and policy, textbooks, land use, and national land theory. Heritage is a family business.
 Corporealizing Moroccan Place
Corporealizing Moroccan Place
I wondered—how does a person become a place? A street, city quarter, mosque, or town could take the name of the wali interred there, like the cities of Sidi Slimane and Mawlay Idris. The sacred enters physical space through the body.
 Material Economies of Life-Time: Grief, Injury, Expiation, Desire
Material Economies of Life-Time: Grief, Injury, Expiation, Desire
Tracy Fessenden, Hillary Kaell, and Alexia Williams discuss three iterations of religious, material economies: bus stop clocks, cloistered Magdalens, and a Catholic prayer card from Denver.
 A Photograph in Words
A Photograph in Words
In her memoir, The Red Parts, Maggie Nelson writes about the over-thirty-year-old unsolved murder of her aunt, Jane Mixer, a case brought back to life in a Michigan court room. Who gets to tell this story? How should it be told?
 Pausing on a Sunday: What Kind of Secular is the American Musical?
Pausing on a Sunday: What Kind of Secular is the American Musical?
The musical in which this song appears includes archetypal depictions of the modern artist and his attendant gendered capacities and failures. Sondheim would point out: its lyric is a single sentence; it is a description of a process; it includes a word, “forever,” that he observes makes him cry.
 A Closing Conversation
A Closing Conversation
If the Marxian dialectic culminates with the mystification of the commodity, these essays seem to envision a sacralization and re-sacralization of the profane, such that matter is the accumulation of sacred value. Transcendence and enchantment in this account are very much “real” and just as ontologically entrenched as capitalism.
 The Intimate Ironies of the Wifey: Material Religion and the Body
The Intimate Ironies of the Wifey: Material Religion and the Body
From the familiarity of scent to the spread of colonial/space time, and through Black vernacular culture and “linking” us to divine power through the digital, Ellen Amster, Dusty Gavin, and Suzanne van Geuns introduce us to the strange intimacies of the wifey.
 Designing Risk, Accumulating Failure: Purgatory, the Planned, and Primitive Accumulation
Designing Risk, Accumulating Failure: Purgatory, the Planned, and Primitive Accumulation
In Fall 2020, Paul Johnson, Emily Floyd, and Kati Curts met on Zoom. In this edit of their extended conversation, the authors question “planned sacred space,” the role of design in creating religious experience, and the category of the “relic.”
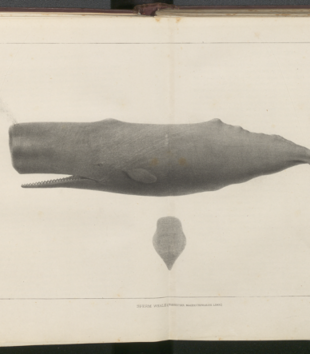 The Old Gods: Whales, Oil, and Teak
The Old Gods: Whales, Oil, and Teak
Judith Ellen Brunton, Richard Callahan, and Alexandra Kaloyanides endeavor to find the resonances their images pose to characterizing material economies of religion in the Americas. In emails from the autumn of 2020, each offers moments of speculation on the contexts shaping their research objects, and the supernatural powers and economies they enchant.
 American Performances, Economies, and Genealogies of Constraint
American Performances, Economies, and Genealogies of Constraint
In this collaboratively written exercise, the authors discuss the material significance of embodied sense perceptions and affects. Despite Protestant secularity’s claims to the contrary, sensation and affect are no more confined to interiorized subjective mental states than is religion merely belief.
 Sperm Whale Teeth in Circulation: A Case Study in Material Economics
Sperm Whale Teeth in Circulation: A Case Study in Material Economics
From Fijian ceremonial objects to nineteenth-century American whaling souvenirs, to airline membership cards, this constellation explores material economies through one raw material: sperm whale teeth.
 “Colored Magdalens,” House of the Good Shepherd for Colored Girls, Baltimore, ca. 1930s
“Colored Magdalens,” House of the Good Shepherd for Colored Girls, Baltimore, ca. 1930s
Was [the Magdalens'] decision to own in perpetuity the status of penitent a judgment on waywardness, or a benediction? An internalization of white surveillance, or its repudiation?
 Let. It. Burn. SoulCycle's Jonathan Adler Grapefruit Scented Candle
Let. It. Burn. SoulCycle's Jonathan Adler Grapefruit Scented Candle
While a stationary bike is the main conduit for the SoulCycle experience, perhaps no object plays a greater role in facilitating SoulCycle’s choreography of emotion than the brand’s signature grapefruit-scented candle.
 The Currency of Religion in America in Three Acts: Market Logics, Emissaries of Kinship, and Technologies of Feeling
The Currency of Religion in America in Three Acts: Market Logics, Emissaries of Kinship, and Technologies of Feeling
Cody Musselman, Kambiz GhaneaBassiri, and Roxanne Korpan each present an object for consideration. Together they think about what it means for each object to be involved in the material economy of religion. Their conversation traverses various geographies and traditions, and ponders how material objects can be carriers of religion.
 The Sticky Cookies of Biblical Womanhood
The Sticky Cookies of Biblical Womanhood
Biblical womanhood blogs often resemble the idealized Christian home they encourage women to build. Businesses have long recognized the potential for profit in networked domesticity, enticing bloggers to participate in commercial enterprise by promising percentages of purchase costs made through their sites.
 eBay Buddha
eBay Buddha
This golden Buddha, which has a striking resemblance to a Burmese Buddha in the British Museum, came up for sale on eBay for the sum of $5,000.00. The material of teak, the economies of the British and Burmese empires, the religion then being named "Buddhism," now give us this American eBay Buddha.
 Wifey
Wifey
The fragrance Wifey by KKW Fragrances was released in 2019. As wife to black artist Ye (formerly Kanye West), Kim KW claimed and sold the role of wifey. The “wifey” is not simply a wife. She is a model or caricature of a wife, a down-ass. The “wifey” signifies a new ideal in our contemporary popular culture.
 Making Paths with Stone
Making Paths with Stone
Eshu-Elegguá is a divinity in the Regla de Ocha-Ifá pantheon characterized as a warrior and messenger. Enslaved Africans in Cuba taught their descendants that a good relationship with this divinity is helpful for making risky choices and providing protection when embarking on a treacherous new beginning.
 Fuel for the Soul
Fuel for the Soul
The bible "God's Word for the Oil Patch: Fuel for the Soul" offers insight into how people theorise both the value of energy and the kind of lives people need to live to access this value. The publication implies that to have the kind of soul that lives a good life, you need to manage oil and its energy: souls are things that need fuel, be it "God's word" or oil itself. Oil work, in this context, becomes soul work.
 Bus Station Clocks
Bus Station Clocks
A row of clocks. Each one with an identical, nondescript face—except for the hands, which are conspicuous in their different orientations. Clocks are the kind of “religion” that spills out beyond the sphere of the sacred. Rows of clocks that evoke utopian, aspirational feelings of global connectedness. These are “religious” feelings in the deepest sense of the term.